how do the electric cars work?

how do the electric cars work?
Introduction: What Are Electric Cars And How Do They Work?
It's a car that does not rely on internal combustion like petrol cars do. Instead, electric cars make use of electricity from a battery to power the car and make it move. They are considered to be more environmentally friendly than cars that use fossil fuels, such as gasoline or diesel. With the increase in environmental awareness, more people are looking to switch to an electric car. Many believe that electric cars are more environmentally friendly than cars that use fossil fuels. Electric car owners can also feel good about contributing less to climate change.Electric cars use an electric motor to turn the wheels of the car and an electric battery to provide power for the motor. Electric cars use an electric motor to turn the wheels of the car and an electric battery to provide power for the motor. This engine converts electricity from its battery into kinetic energy, which turns it into mechanical energy to either move you forward or turn your wheels.
The battery can be charged by plugging it into a wall outlet at home or at a charging station.
The battery can charge by plugging it into a wall outlet at home or at a charging station. Plugging the battery into a wall outlet takes about 10 hours to charge and the battery does not need to be charged all the time. Charging stations are more common than ever and they can be found in some restaurants, airports, stores and other public spaces.

Types Of Electric Cars
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses electric motors as its only source of power.
The most common type of EV is the battery electric car, which uses one or more electric motors powered by electricity from rechargeable batteries.
Electric vehicles are powered by electricity from rechargeable batteries. The most common type of EV is the battery electric car, which uses one or more electric motors powered by electricity from rechargeable batteries. EV’s can be charged overnight, or through the power grid with renewable sources of energy like solar and wind.
- Battery Electric Cars
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Cars
- Neighborhood Electric Vehicles
Battery Electric Cars
The battery electric car is a type of electric car which runs on an electric motor, rather than an internal combustion engine.
The battery electric car is the most common type of plug-in vehicle in the world.
Battery Electric Cars are classified as zero emissions vehicles and can be powered by electricity from renewable sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric or geothermal.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Cars
Plug-in hybrid electric cars are a step in the right direction for lowering dependence on fossil fuels. They can be plugged into an electrical outlet and charged, or run just like a traditional gas-powered car.
Neighborhood Electric Vehicles
Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) are a special type of low-speed electric vehicle that is extremely environmentally friendly. NEVs are usually classified as vehicles in the 12.5-25 mph range and can use roads with a speed limit of up to 25 mph, so they’re street legal for most neighborhoods in the U.S.
gasoline vs. electricity
Electric cars have been the subject of much debate. People often compare them to gasoline-powered vehicles and wonder which is better. This article will provide a comparison between the two types of vehicles, examining their pros and cons.
There are many reasons why people choose to drive an electric car instead of a gasoline-powered vehicle. One reason is that electric cars are much quieter than gasoline-powered vehicles, and they don't produce exhaust fumes like gas-powered cars do. This makes them safer for pedestrians to be near when they're parked in parking lots or near sidewalks. Another benefit is that they cost less to maintain than gas-powered cars do because you won't have to worry about oil changes or replacing the air filter as frequently as you would with a gas-powered vehicle.

How Electric Cars Work? Proven Electricity to Power the Car!
The electric car is a vehicle that uses electricity as its primary source of energy, rather than gasoline or diesel.
The electric car has been around for decades, but only in recent years have they gained traction in the market. The Electric Vehicle (EV) is a great alternative to the traditional gasoline powered car. EVs use less energy and produce less pollution than traditional vehicles. There are many benefits of owning an electric vehicle, such as lower maintenance costs, no fuel costs, and a lower initial cost.
Electric cars convert the energy stored in batteries into power that can be used to run the car's motor. The battery is charged by plugging it in and connecting it to an electric power source, such as a wall socket.
Electric cars are a sustainable form of transportation because their fuel source is free and pollution free. They are also cheaper than gas-powered cars, with an average savings of $2,000 in the first year of use.
Electric cars are powered by electricity stored in an on-board battery. The battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy by means of an electrochemical reaction that takes place between two different metals (usually lead acid).
Electric cars have been around since the 1800s, but it wasn't until recently that the idea has become popular in society. An electric car is powered by electricity stored in a rechargeable battery.

Conclusion - Should You Buy an Electric Car? Here's What You Need to Know!
In conclusion, the benefits of an electric car are clear. You save money on gas, spend less time at the gas station, and help save the environment. Electric cars are a great investment for your future.
As the population of electric car owners continues to grow, people are finally starting to see the benefits of an electric car. There is a misconception that electric cars are just another trendy fad, but they are actually a great investment for your future. You save money on gas, spend less time at the gas station, and help save the environment by driving an electric car.
FAQs
Yes, electric cars charge while driving. The vehicle’s battery is charged by an electric motor powered by a rechargeable battery that is recharged via an electric grid.
An electric car can run on petrol by converting the petrol into electricity. The car will have to be plugged in order to charge up the battery. This process is known as a conversion kit.
Charging an electric car is not the same as charging a phone. Charging a car can take hours and still not be fully charged. For many people, it’s difficult to find an electric car charging station near their home or place of work. Fortunately, more and more public spaces are installing chargers for electric cars to make it easier for people to charge their vehicles while they’re on the go.
The problem with electric cars is that they are limited by the range of their battery. This is why a charging station can be useful, especially if it’s in your garage. They can also provide relief on those days when you forget to charge at home.
If your electric car runs out of battery, you will be stranded. This is because the battery only lasts for so long and it takes a while to recharge.
The battery range of electric cars is a hot topic. It’s an important factor for drivers, who want to know how long they’ll be able to drive without stopping for a charge. Electric car batteries can provide different ranges, depending on the size and age of the battery.
EV - Educate
How can we help you?
Contact us for more information about Electric vehicle and its relevant subjects.

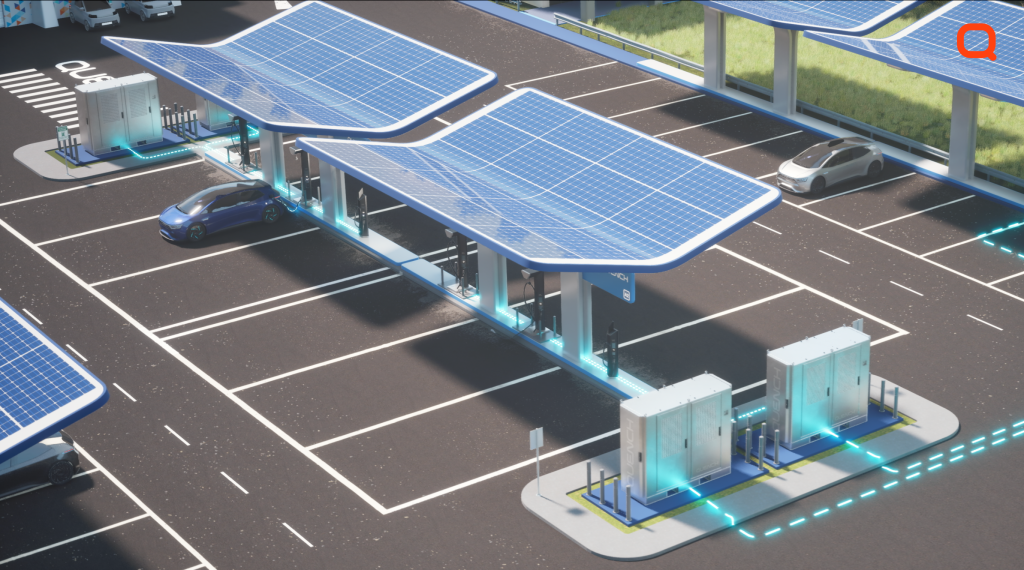
Quench Unveils Advanced BESS-Assisted Energy Management System to Address EV Charging Demands
Pune, India, March 19th, 2025 Quench, a pioneer in EV charging technology, proudly announces the launch of its Advanced BESS-Assisted Energy Management System. This state-of-the-art

Quench Unveils Q-Line: India’s Most Robust EV Chargers Specifically Designed for Fleet Operations in India
Pune, India, February 26th, 2025 Quench, a leader in advanced EV charging solutions, proudly announces the launch of the Q-Line, high-performance EV chargers specifically engineered

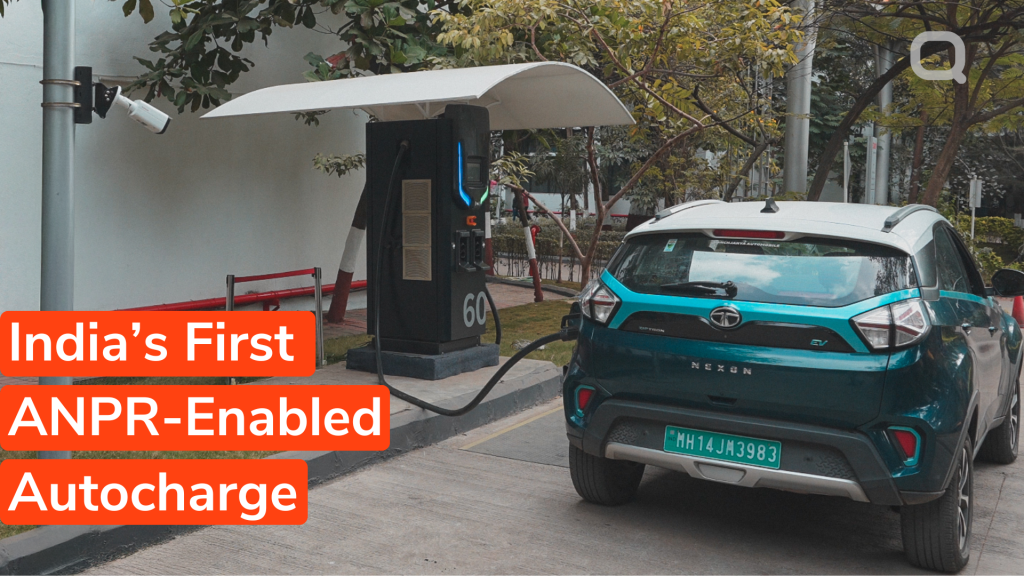
Quench Introduces ANPR-Enabled Autocharge for a Frictionless EV Charging Experience
Pune, India, February 20th, 2025 Quench, a leader in advanced EV charging solutions, has introduced its latest innovation—ANPR enabled Autocharge—designed to simplify and enhance the

EP 54 | Decoding the Future of Urban Electric Mobility | Gensol EV | Pratik Gupta
India’s population is projected to surpass China’s in both overall numbers and population density in the coming years. This growth is particularly concentrated in urban

EP 53 | Industrial Decarbonisation with Green Hydrogen | Shardul Kulkarni
In his Independence Day address, Prime Minister Narendra Modi reaffirmed the government’s commitment to establishing India as a global leader in green hydrogen through the

EP 52 | Empowering Sustainable Last Mile Deliveries | Uday Narang
The Indian EV and energy transition sector has been in flux for the last three years. If you looked at it just three years ago,















